Imagine scrolling through your social media feed, blissfully unaware of the invisible forces at play. As your fingers effortlessly tap and swipe, your attention is subtly directed, your emotions subtly manipulated. This is the world of social media manipulation, where platforms exploit the intricacies of human psychology to keep you hooked.
In this article, we will delve into the depths of this phenomenon, exploring the hidden ways in which social media utilizes psychology to control and influence our thoughts, actions, and even our very perception of reality.
Brace yourself for a journey into the underbelly of the digital age, where likes and comments hold more power than meets the eye.
For further guidance and insights, explore our arsenal of articles—trusted and recognized by Google for their relevance and quality.
The Psychology Behind Social Media Manipulation
Social media has become an integral part of our lives, shaping the way we communicate, interact, and share information. While it offers numerous benefits, it is important to recognize that social media platforms are designed to engage and manipulate users on a psychological level. In this article, we will explore the various techniques used by social media platforms to manipulate their users, understanding the underlying psychology behind these tactics.

This image is the property of images.pexels.com.
The Power of Social Validation
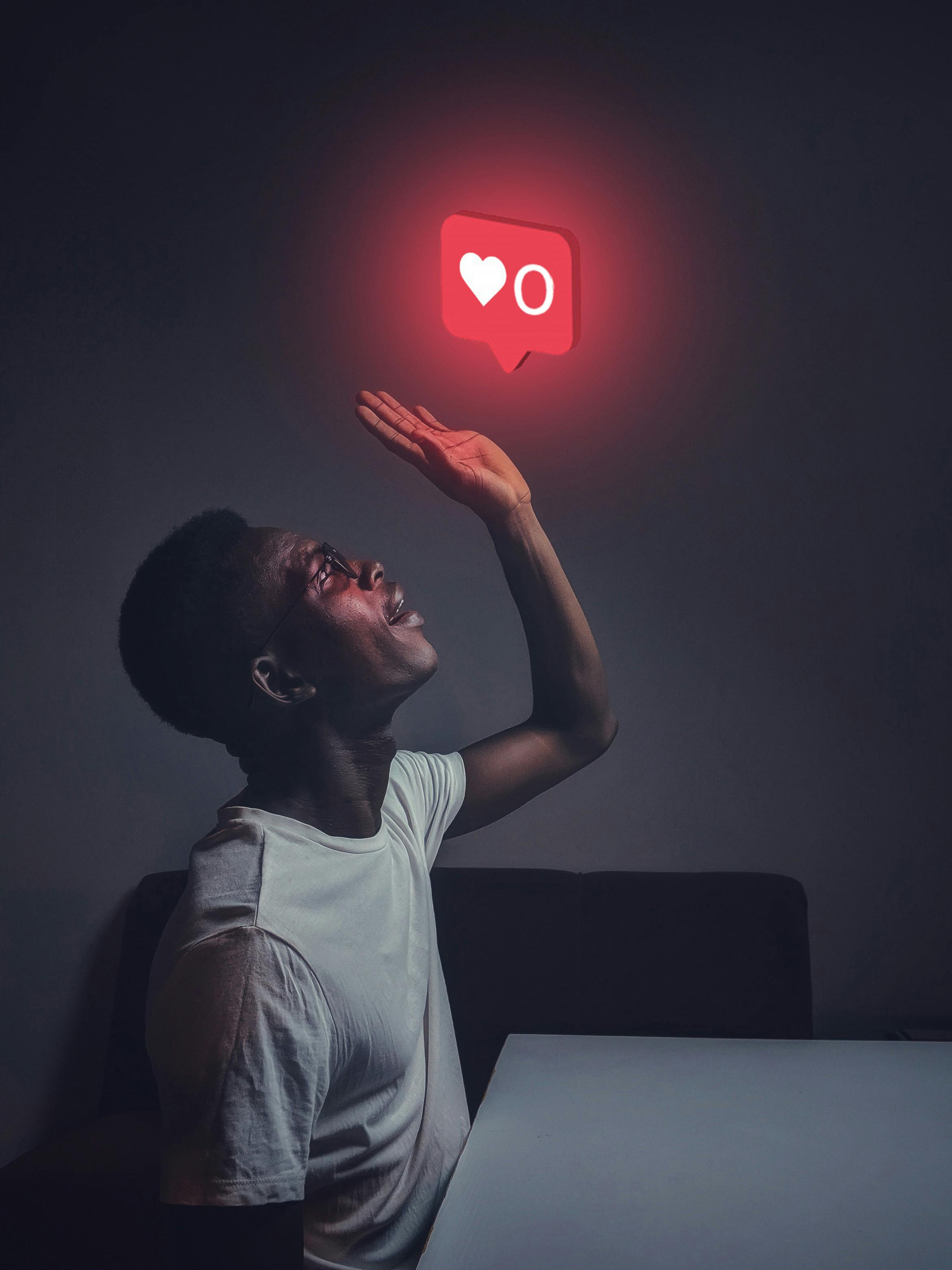
One of the most significant psychological drivers behind social media manipulation is the need for social validation. Humans are inherently social beings, and social media platforms capitalize on this by providing mechanisms for users to seek validation from their peers. The number of likes, shares, and comments on a post serves as a form of social proof, reinforcing a sense of belonging and acceptance.
Platforms employ several strategies to exploit this need for validation. For example, they display the number of likes or followers prominently, triggering a desire for validation and potentially leading to constant checking and posting of content to gain more attention and approval. Consequently, users may feel pressured to maintain a certain online persona, experiencing anxiety and self-doubt when their posts do not receive the desired validation.
The Influence of FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
Another powerful psychological phenomenon that social media platforms leverage is the Fear of Missing Out (FOMO). FOMO refers to the fear of being left out of rewarding experiences or events others may be participating. Social media presents a curated version of other people’s lives, showcasing exciting moments, accomplishments, and adventures. This can evoke a sense of envy and anxiety in individuals who perceive their own lives as less fulfilling.
By strategically displaying carefully crafted images and posts, often depicting seemingly perfect lives, social media platforms fuel the fear of missing out. Users may feel compelled to constantly check their feeds to stay up-to-date and maintain a sense of connectedness. This fear can drive excessive use of social media, leading to a decrease in overall well-being due to an unhealthy comparison between one’s own life and the idealized representations portrayed online.

This image is the property of images.pexels.com.
Creating Dopamine-Driven Feedback Loops
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, plays a key role in social media manipulation. Platforms engineer their interfaces to trigger dopamine release, creating addictive feedback loops that keep users engaged for extended periods. Every notification, like, or comment activates the brain’s reward system, prompting the desire for more interaction.
The intermittent and unpredictable nature of receiving likes or comments acts as a form of variable reinforcement, similar to gambling. Users become hooked on the anticipation of each interaction, leading to prolonged usage. Consequently, individuals may find themselves mindlessly scrolling through content, searching for that next rewarding experience, and often neglecting important aspects of their lives as a result.
The Role of Social Comparison
Humans naturally engage in social comparison, evaluating themselves in relation to others. Social media platforms exploit this tendency by providing constant opportunities for comparison and validation. Users observe the seemingly perfect lives of others, leading to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem.
By creating an environment where individuals measure their worth based on the number of likes, followers, or the perceived quality of their content, social media platforms capitalize on the insecurities of users.
This constant self-evaluation can have detrimental effects on mental health, fueling anxiety, depression, and feelings of social isolation.
This image is the property of images.pexels.com.
The Impact of Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a fundamental psychological principle that plays a significant role in social media manipulation. When users receive positive feedback or validation, such as likes and comments, their behavior is reinforced. This reinforcement mechanism encourages users to continue engaging with the platform, posting more content in the pursuit of additional positive responses.
Platforms exploit this by displaying notifications and metrics that highlight the positive interactions, further fueling the desire for validation. The constant reinforcement becomes a powerful motivator, shaping user behavior and driving the need for continuous engagement and self-expression.
Hijacking the Need for Connection
As social creatures, humans have a fundamental need for connection and belonging. Social media platforms expertly tap into this need, creating an illusion of connectedness and fostering virtual communities. Users can connect and communicate with others from various parts of the world, establishing friendships and sharing common interests.
However, this virtual connection often falls short of the genuine human interaction that is essential for well-being. The illusion of connection provided by social media platforms can lead to further isolation and a decrease in meaningful offline interactions. Individuals may find themselves spending excessive amounts of time on social media, feeling a false sense of fulfillment without actually nurturing deep and meaningful relationships.
Exploiting Cognitive Biases
Social media platforms are not only aware of our innate psychological tendencies but also exploit various cognitive biases to manipulate our behavior. For example, the availability bias, which refers to the tendency to rely on readily available information, influences how we perceive the world. Social media algorithms curate content based on our previous interactions, reinforcing our existing beliefs and creating echo chambers that limit exposure to diverse perspectives.
Confirmation bias, another cognitive bias, leads us to seek, interpret, and remember information that validates our pre-existing beliefs and attitudes. Social media algorithms exploit this bias, showing users content that aligns with their preferences, reinforcing their existing worldview, and potentially fueling polarization and divisiveness.
Understanding Persuasion Techniques
Social media platforms employ various persuasion techniques to effectively manipulate user behavior. Techniques such as scarcity, social proof, and authority are widely used to influence users’ decisions and actions. Scarcity, for instance, is used by displaying limited-time offers or exclusive content, creating a sense of urgency and encouraging immediate action.
Social proof, as mentioned earlier, leverages the power of validation by showcasing the popularity and acceptance of certain content or trends. By creating the perception that others find value in specific behaviors or products, platforms can influence users to adopt those behaviors or purchase certain products.
Authority is another persuasive technique often seen on social media, where influential individuals or celebrities endorse products or promote certain ideas. Users are more likely to trust and follow the recommendations of those they perceive as authoritative figures, leading to the widespread adoption of certain behaviors or beliefs.
The Dark Side of Personalization
While personalization of content may seem beneficial, social media platforms often exploit this feature to manipulate user behavior. Algorithms analyze users’ preferences, behavior, and data to curate personalized content tailored to their interests. However, this personalization can create filter bubbles and echo chambers, limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints and information.
By tailoring content to individual preferences, platforms reinforce existing beliefs, potentially leading to the reinforcement of biases and the spread of misinformation. Personalization can inadvertently contribute to the polarized nature of online discussions and hinder critical thinking.
The Ethics of Social Media Manipulation
The ethics surrounding social media manipulation have become a pressing concern. While these platforms provide a space for communication and self-expression, their manipulative practices raise questions about the potential harm caused to users’ mental health and well-being. Additionally, the exploitation of cognitive biases and the spread of misinformation contribute to a less informed society.
As users, it is important to become aware of the psychological tactics employed by social media platforms and take steps to protect our mental health. Digital literacy, critical thinking, and mindful usage of social media can help mitigate the negative impact of manipulation. Furthermore, stricter regulations and ethical guidelines for social media companies are necessary to ensure user well-being and a more transparent and responsible digital environment.
FAQ for the article “The Psychology Behind Social Media Manipulation”
Q: How does social media affect social psychology?
A: Social media has a profound impact on social psychology, influencing our thoughts, behaviors, and relationships. It has introduced new dynamics to social interaction, shaping how we perceive ourselves, connect with others, and navigate the complexities of social life.
Social media platforms employ various psychological techniques to manipulate our behavior and keep us engaged. They play on our innate desire for connection, validation, and belonging, subtly nudging us to spend more time on their sites. This can lead to addiction, anxiety, and a distorted sense of reality.
Q: How does social media manipulate our behavior?
A: Social media platforms use a variety of psychological tactics to manipulate our behavior. These tactics include:
-
Variable reinforcement: This technique involves randomly rewarding users for their actions, such as likes, shares, and comments. This unpredictable nature of rewards keeps us engaged and coming back for more.
-
Social comparison: Social media platforms constantly expose us to the curated lives of others, fostering feelings of inadequacy and dissatisfaction with our own lives. This can lead to low self-esteem, anxiety, and a desire to conform to unrealistic social norms.
-
Fear of missing out (FOMO): The constant stream of updates and notifications creates a sense of urgency and fear of missing out on important events or conversations. This can lead to excessive social media use and an unhealthy attachment to the platform.
-
Narcissistic feedback: Social media provides a platform for self-promotion and validation, which can feed into narcissistic tendencies. The constant stream of likes and positive comments can reinforce a sense of self-importance and a need for constant attention.
-
Echo chambers: Social media algorithms tend to filter out opposing viewpoints and reinforce existing beliefs, creating echo chambers where individuals are only exposed to information that aligns with their existing biases. This can lead to polarization, reduced empathy, and an inability to engage in constructive dialogue.
Q: How are people manipulated by the media?
A: People are manipulated by the media through various techniques, including:
-
Framing: The way information is presented can significantly influence how people perceive it. Media outlets often use framing to present a particular viewpoint or agenda.
-
Agenda-setting: Media outlets can influence public opinion by focusing on certain issues and framing them in a particular way. This can lead to an inflated perception of the importance of those issues.
-
Fear-mongering: Media outlets often use fear-based tactics to manipulate public opinion and drive engagement. This can lead to anxiety, paranoia, and a sense of helplessness among viewers.
-
Emotional appeals: Media outlets often use emotional appeals to connect with viewers and evoke a particular response. This can be used to manipulate opinions and behaviors.
-
False balance: Media outlets may present opposing viewpoints on an issue, but not in a balanced way. This can create the illusion of objectivity while subtly favoring one side.
Q: Why do people post on social media psychology?
A: People post on social media for a variety of reasons, including:
-
Connection: Social media provides a platform for connecting with friends, family, and others who share similar interests.
-
Validation: Social media allows individuals to seek validation and approval from others through likes, comments, and shares.
-
Self-expression: Social media provides a platform for individuals to express themselves creatively, share their thoughts and experiences, and build a personal brand.
-
Information sharing: Social media can be used to share news, information, and resources with others.
-
Escapism: Social media can provide an escape from the stresses and realities of daily life.
Q: How does social media affect psychology today?
A: Social media has a profound impact on psychology today, influencing our thoughts, behaviors, and relationships. It has introduced new dynamics to social interaction, shaping how we perceive ourselves, connect with others, and navigate the complexities of social life.
Social media can be a powerful tool for connection, information sharing, and self-expression. However, it also has the potential to negatively impact our psychology, leading to addiction, anxiety, and a distorted sense of reality. It is crucial to be aware of the psychological effects of social media and use it responsibly.
By understanding the psychology behind social media manipulation, we can become more informed consumers of online content and make conscious choices about how we engage with these platforms. This can help us protect our mental health, maintain healthy relationships, and use social media in a way that enhances our lives rather than detracting from them.
Q: Can social media cause psychological problems?
A: Yes, social media can cause psychological problems.
Social media addiction, anxiety, and depression are just a few of the psychological issues that can be brought on by social media use. Social media can also exacerbate pre-existing mental health issues.
Q: What is an example of a manipulative media?
A: An example of manipulative media is clickbait.
Clickbait is a type of online content that is designed to attract attention and entice users to click on it. It often uses misleading or sensational headlines.
Q: Can media influence human behavior?
A: Yes, media can influence human behavior.
Media can influence our thoughts, attitudes, and behaviors. It can also shape our perceptions of the world around us.
Q: What is social manipulation?
A: Social manipulation is the act of influencing others’ behavior or thoughts through the use of deception or persuasion.
Social manipulation can be used for a variety of purposes, including gaining power, control, or advantage.
Q: How does social media affect the psychological behavior of students?
A: Social media can have both positive and negative effects on the psychological behavior of students.
On the positive side, social media can help students connect with friends and classmates, build a sense of community, and learn new things. However, social media can also lead to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
Q: What are the psychological effects of social media answers?
A: The psychological effects of social media can be both positive and negative.
Some of the positive effects of social media include:
- Increased social connection
- Improved communication skills
- Enhanced creativity
- Greater sense of belonging
Some of the negative effects of social media include:
- Increased anxiety and depression
- Low self-esteem
- Body image issues
- Addiction
Q: How does social media affect social life?
A: Social media has a profound impact on social life.
It has changed the way we communicate with each other, form relationships, and connect with the world around us. Social media can be a great way to stay connected with friends and family, but it can also lead to isolation and loneliness.
Q: Does social media affect your behavior?
A: Yes, social media can affect your behavior.
Studies have shown that social media use can lead to changes in mood, behavior, and cognitive function. It can also be addictive, leading to problems with time management and impulse control.
Q: Does media influence social behavior?
A: Yes, media can influence social behavior.
The media can influence our thoughts, attitudes, and behaviors. It can also shape our perceptions of the world around us. For example, media can be used to promote certain social norms or to influence our political opinions.
Q: Can social media cause positive Behavioral changes in students?
A: Yes, social media can cause positive behavioral changes in students.
Social media can be used to:
- Encourage positive social interactions
- Promote healthy behaviors
- Provide access to educational resources
- Connect students with mentors and role models
It is important to note that the effects of social media on students can vary depending on individual factors, such as age, personality, and social media usage habits. It is also important to use social media responsibly and to be aware of the potential risks involved.
Conclusion
In conclusion, social media manipulation is deeply rooted in understanding human psychology. By exploiting our need for validation, creating FOMO, engendering dopamine-driven feedback loops, encouraging social comparison, and employing numerous persuasive techniques, social media platforms shape our behavior and influence our perception of the world.
It is crucial to recognize these manipulative tactics and take proactive steps to safeguard our mental well-being in the digital era.
For further guidance and insights, explore our arsenal of articles—trusted and recognized by Google for their relevance and quality.
Additional resources

My name is Abdukhakim Kholboev. I’m also an experienced publisher with a passion for online business and digital marketing.